PYRAMID STRUCTURE- Roles and responsibilities of different levels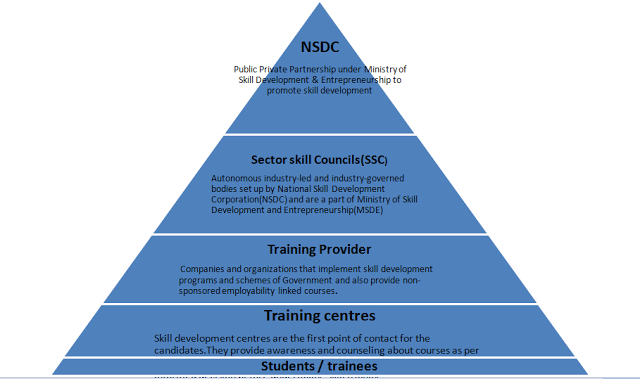 Role of NSDC
Role of NSDC
Funding and incentivising: This is a key role. This involves providing financing either as loans or equity, providing grants and supporting financial incentives to select private sector initiatives to improve financial viability through tax breaks, etc. The exact nature of funding (equity, loan and grant) will depend on the viability or attractiveness of the segment and, to some extent, the type of player (for-profit private, non-profit industry association or non-profit NGO). Over time, the NSDC aspires to create strong viable business models and reduce its grant-making role
Enabling support services: A skills development institute requires a number of inputs or support services such as curriculum, faculty and their training, standards and quality assurance, technology platforms, student placement mechanisms and so on. The NSDC plays a significant enabling role in some of these support services, most importantly and in the near-term, setting up standards and accreditation systems in partnership with industry associations
Shaping/creating: In the near-term, the NSDC will proactively seed and provide momentum for large-scale participation by private players in skill development. NSDC will identify critical skill groups, develop models for skill development and attract potential private players and provide support to these efforts.
Role of SSC
o Creation of Qualification Packs(QP) pertaining to different job roles identified in the respective sectors
o Creation of National Occupational Standards (NOS) applicable for each and every QP
o Determining competency standards and qualifications and getting them notified as per National Skills Qualification Framework(NSQF)
o Participation in the setting up of affiliation,accreditation, examination and certification norms for the respective sectors.
o Plan and facilitate the execution of training of trainers and their certification
o Affiliation of training and assessment companies for conducting skill development courses in their respective sector
o Assessment and Certification of trainees
o Conduct skill gap studies in their sectors and help in making Labor Market Information System
o Ensure employment of trainees trained and certified as per the norms
Role of Training providers
o Implementation of skill development schemes and programmes
o Creation, arrangement of physical infrastructure, training equipment and labs
o Preparation of curriculum, content,training and teaching material
o Recruitment, development, and deployment of trainers and support staff
o Mobilization of financial and non-financial resources for smooth execution of training programmes
o Awareness, outreach, and propagation of skill development courses offered by them
o Tie up with industry/employers for on the job training and placement opportunities for candidates after completion of training
o Disbursement of stipend and post placement support money offered by some schemes to the participants
o Post placement tracking of the candidates
Role of Training Centers
o First point of contact for the candidates
o Provide awareness and counseling about courses as per the qualification and interest of the candidates to help them take an informed decision before undertaking skill training.
o In the present skill development ecosystem, representatives of the training centre(mobilizer,counselor or influencer) explain the courses offered and programmes and schemes under which a candidate can enroll for training.
o Provide opportunities for classroom and practical training, peer and industry interaction, employability and soft skill training and finally the placements.
o Training centres have the maximum responsibility in successfully implementing skill development courses and programmes. A well-established and efficiently managed training centre is an asset and a profit centre for a training provider.
